Series
Understanding the Risks of Oversharing in Microsoft 365
1: Guest Account and Internal User Security Risks in Microsoft 365: How to Prevent Data Exposure (you are reading this article)
2: Preventing Unauthorized Access to Shared Mailboxes and Distribution Lists in Microsoft 365
3: Microsoft Teams Oversharing Problem: How to Protect Your Data
4: Microsoft 365 Copilot and Data Security: Are You at Risk of Oversharing?
Microsoft 365 offers powerful tools like SharePoint Online, OneDrive, Teams, Shared Mailboxes, Distribution Lists, and AI-powered Copilot to streamline collaboration. But with all this convenience comes a hidden danger: oversharing.
When sensitive information lands in the wrong hands—whether due to weak security settings, excessive permissions, or accidental sharing—it can lead to data breaches, compliance violations, or financial losses.
This is the first article in a four-part series about the risks of oversharing in Microsoft 365 and how to prevent them. We’ll begin by exploring guest account and internal user security risks, then dive into unauthorized access to shared mailboxes and distribution lists, uncover the unique risks of oversharing in Microsoft Teams and finally, examine Copilot’s security and compliance challenges.
Let’s kick off Part 1 by looking at how guest accounts and internal users can put your data at risk and what you can do to keep it secure.
Key Risks Posed by Guest Accounts and How to Mitigate Them
Guest accounts allow external partners, contractors, or vendors to access organizational resources, but they can also introduce substantial security concerns. To minimize these risks, organizations need to be mindful of the following issues:
1. Excessive Access to Sensitive Data
External guests may inadvertently gain access to confidential information if granted excessive permissions on SharePoint, OneDrive, or Teams channels. For example, a vendor with access to a Teams channel might download a file containing proprietary financial forecasts that were mistakenly left accessible.
Mitigation: Regularly review and limit guest permissions to only the essential resources. Set time-bound access for external users and promptly decommission guest accounts when collaboration ends. Require Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all external users to enhance security. Additionally, consider implementing sensitivity labels on files to reduce the risk of accidental sharing of sensitive information.
2. Lack of Accountability
Monitoring guest activities is often more challenging than for internal users, making it harder to identify potential misuse or unauthorized sharing of information. Imagine a scenario where an external contractor downloads sensitive project data, but the activity goes unnoticed due to insufficient tracking.
Mitigation: Assign a sponsor to each guest account, making them the primary contact for the guest. This enables you to schedule regular access reviews, where sponsors can confirm whether the guest still needs access to company resources. Set time-bound access for guest accounts, ensuring they only have access for as long as necessary, and implement processes to decommission guest accounts once their collaboration ends.
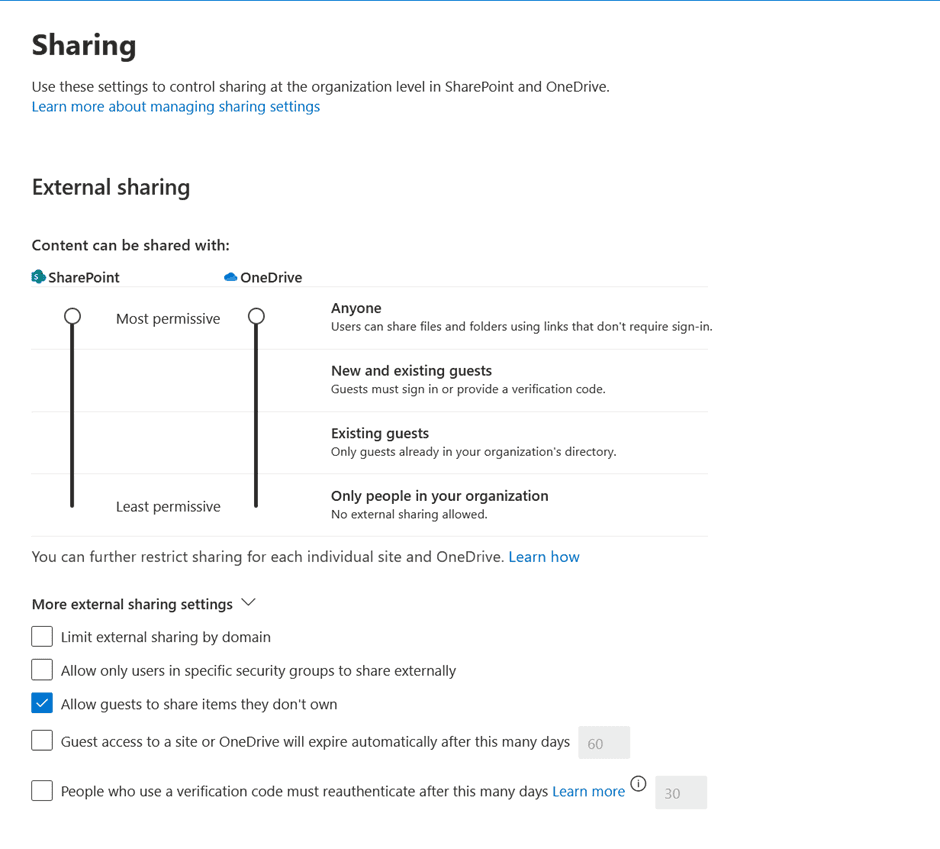
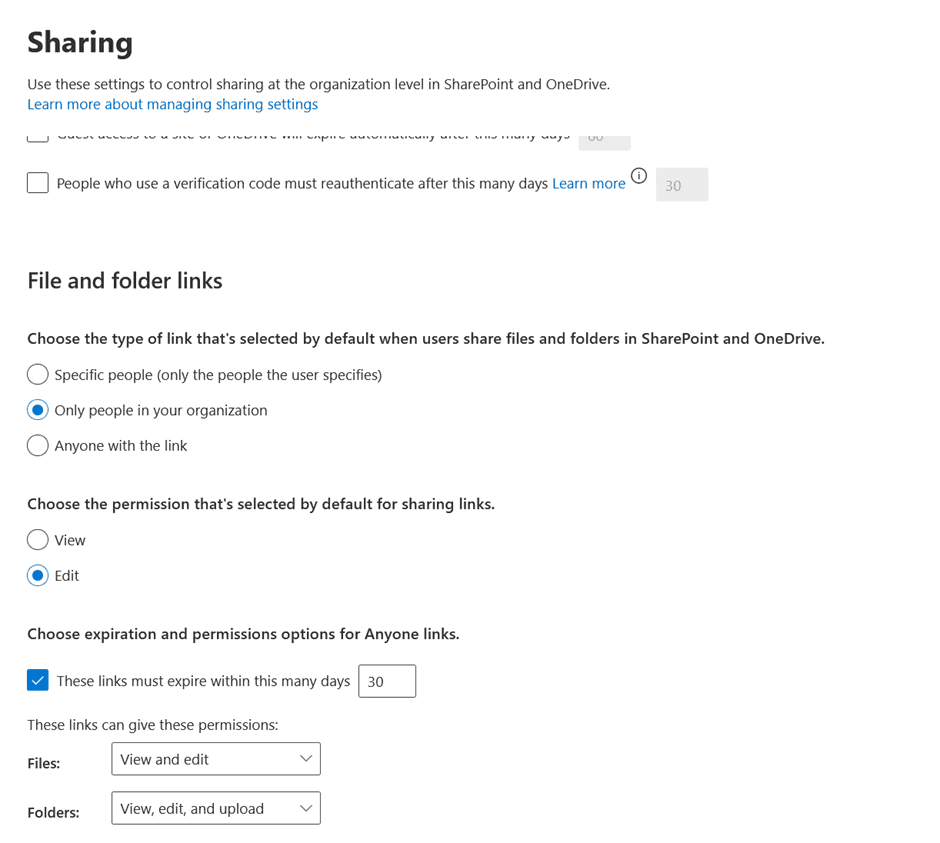
3. Insecure Sharing Links
Guests may receive links with broad access (e.g., "Anyone with the link"), which can be forwarded to unauthorized parties, putting sensitive data at risk. For example, an external partner shares a link with their colleague outside the organization, who then accesses confidential materials.
Mitigation: Update the default sharing settings in the SharePoint Admin Center by disabling the option "Allow guests to share items they don’t own.”
Additionally, configure "Anyone" links to automatically expire after a specified duration to enhance security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Note that these settings apply to the entire tenant. You can specify dedicated settings for each individual SharePoint site.
While guest accounts pose unique challenges, internal users also play a critical role in maintaining security within Microsoft 365. Let's now explore the risks associated with internal user oversharing and how to safeguard against them.
Risks of Internal User Oversharing and How to Mitigate Them
Even though internal users are trusted, they can inadvertently contribute to oversharing if the right safeguards are not in place. Here are some common risks:
1. Accidental Sharing of Sensitive Data
Employees may unintentionally share sensitive documents or files within Teams channels or on OneDrive, often by misconfiguring access settings or sharing with the wrong recipients. For example, an employee shares a report containing confidential client details in a public Teams channel, exposing it to unintended viewers.
Mitigation: Provide training to employees on how to properly configure sharing settings and recognize the risks of improper sharing. Automate sharing controls by applying sensitivity labels at both the container and file levels. Additionally, define clear sharing classifications that outline what can be shared in specific scenarios. This guidance helps users make informed decisions and minimizes the risk of mistakes.
2. Broad Permissions Granted
Granting excessive permissions to internal users, especially on SharePoint sites or Teams channels, can lead to unauthorized access and accidental exposure of sensitive information. For example, a new team member might be given full access to a SharePoint library containing executive-level documents when they only need access to a specific folder. While open communication and transparency are vital in organizations, it’s equally important to minimize the risk of misuse or unintentional errors by carefully managing access permissions.
Mitigation: Adopt the principle of least privilege, ensuring that employees are only given access to the resources they need.
3. Lack of Awareness
Many employees may not fully understand the risks associated with sharing sensitive information or the protocols required to protect that data. For example, an employee might upload sensitive HR documents to a shared OneDrive folder without realizing that it is accessible to all employees.
Mitigation: Regularly conduct security training sessions and enforce clear guidelines around data-sharing practices.
4. Collaborative Over-sharing in Teams
In Teams, users may share entire folders, channel posts, or files without fully considering whether the content is relevant or appropriate for the audience, which can result in overexposure of sensitive information. For example, a project lead might share a folder containing draft contracts and financial analyses, even though only one document is needed for the discussion. While using public Teams is not inherently discouraged, it’s crucial that all users understand these channels are accessible to all employees—and potentially to guest accounts—making careful consideration of shared content even more important.
Mitigation: Encourage users to carefully review the content they’re sharing and limit it to relevant files or documents. More detailed strategies for preventing oversharing in Teams will be covered in the third part of our series.
Don’t Let Oversharing Put Your M365 Environment at Risk
In this first part of our series, we’ve explored the significant security risks posed by guest accounts and internal users in Microsoft 365. These risks—ranging from excessive access to sensitive data to accidental oversharing—can have severe consequences, including data breaches and compliance violations. However, with the right safeguards in place, these risks can be effectively managed and mitigated.
By reviewing guest permissions, implementing accountability measures, and securing sharing settings, organizations can reduce the chance of unauthorized access. Training employees, enforcing access controls, and creating clear sharing guidelines will help keep sensitive information safe.
Solutions like EasyLife 365 Collaboration can help you manage the full lifecycle of collaboration resources, including B2B Guest accounts. EasyLife 365 Collaboration simplifies the process by managing guest access, automating permission reviews, and providing actionable insights to ensure your data stays secure. Remember, securing Microsoft 365 is an ongoing process. As your organization grows and adopts new tools, continuously monitoring and updating security measures is crucial to staying ahead of potential risks.
Stay tuned for Part 2 of our series, which will explore how to prevent unauthorized access to shared mailboxes and distribution lists. In the meantime, make sure you’re taking steps to minimize guest and internal user oversharing to keep your data secure.